1. Overview
Club Connect is an application targeted at club members who are students at the National University of Singapore (NUS). It aims to make the tedious process of club management easier and more effective.
Club Connect is an application that a user who loves to type would fancy - in other words, it uses a Command Line Interface (CLI). All output is displayed on a Graphical User Interface (GUI) - which is just computer jargon for a display that includes panes, menus and message boxes.
2. Purpose of Portfolio Page
This portfolio page describes the contribution I have made to Club Connect’s development – in terms of code, tests, and documentation. It comprises of extracts from the User Guide and Developer Guide, highlighting major and minor features that I worked on during the course of the semester. It also describes some of the other contributions I made – testing, PR reviews, and product management.
3. Summary of Contributions
Major enhancement: Task-Management
What it does: allows users to add, assign, delete and modify tasks.
Justification : Members of a club have certain responsibilities and must carry out tasks to fulfil their responsibilities. Furthermore, EXCO members can delegate tasks to other members which they must perform within a stipulated time period.
Maintaining a record of tasks is crucial as it help maintain transparency and accountability of the club.
Minor enhancements:
-
Added a
Groupattribute toMemberas well as a command to remove aGroupfrom the application. -
Added an auto-complete feature which can be used by pressing the
TAB -
Added email functionality.
Code Contributed : [Functional code] [Test code]
Other contributions:
-
Project Management
-
Managed all releases on GitHub and Milestones.
-
Assumed responsibility of the Team Leader where I took important decisions regarding the product development.
-
-
Documentation
-
Added and improved sections of the User Guide and Developer Guide.
-
-
Features and enhancements
-
Added aliases to existing and new commands - Pull request #159.
-
Added
Groupattribute toMember: Pull Request #66. -
Added
deletetask,viewalltasks, andviewmytasksfunctionality - pull requests #125, #142, and #147.
-
-
Community
-
PRs reviewed (with non-trivial review comments): #53, #67, and #155.
-
Reported bugs and suggestions for other teams during Peer Testing.
-
4. Contributions to the User Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users. |
4.1 Major Enhancement: Task-Management
Start of Extract (from User Guide)
Adding a task: addtask (Since v1.3)
Adds a task to Club Connect.
Format: addtask desc/DESCRIPTION d/DUE_DATE ti/TIME
Aliases: addt, task
| Duplicate tasks are not allowed. |
Examples:
-
addtask desc/Book PGP Function Room 3 d/02/06/2018 ti/19:00
Adds a task with descriptionBook PGP Function Room 3due on02/06/2018at19:00. -
addtask desc/Buy Food d/03.06.2018 ti/15:00
Adds a task with descriptionBuy Fooddue on03/06/2018at15:00.
Changing the status of your task : changetaskstatus (Since v1.5rc)
Changes the status of a task in Club Connect.
Format: changetaskstatus INDEX st/STATUS
Aliases: cts, changestatus, status
|
Tasks are color-coded by status: Yet To Begin In Progress Completed |
Examples:
-
changetaskstatus 1 st/In Progress
Changes the status of the 1st task toIn Progressin the task listing. -
status 3 st/Completed
Changes the status of the 3rd task toCompletedin the task listing.
The three types of statuses are shown below in Figures 12, 13 and 14.



End of Extract (from User Guide)
4.2 Minor Enhancement: Delete Group
Start of Extract (from User Guide)
Deleting a group : deletegroup (Since v1.1)
Deletes the specified group from Club Connect.
Format: deletegroup g/GROUP
Aliases: rmgroup, delgroup
This command is for Exco members only.
|
Examples:
-
deletegroup g/logistics
Deletes thelogisticsgroup from Club Connect. -
deletegroup g/pr
Deletes theprgroup from Club Connect.
Figure 24 shows the output of the deletegroup command.
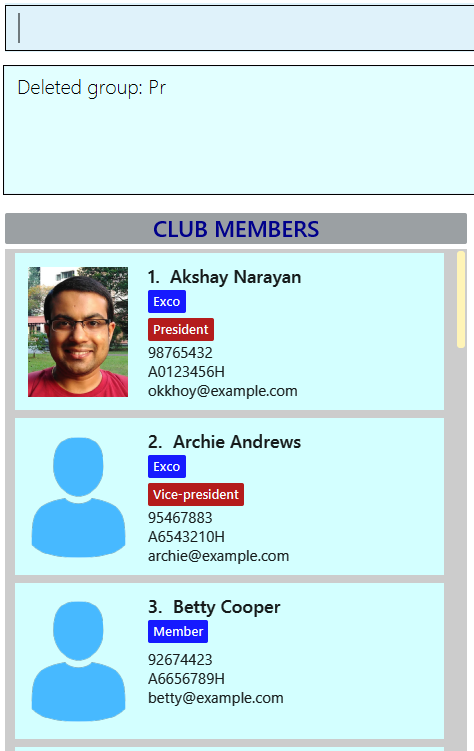
End of Extract (from User Guide)
5. Contributions to the Developer Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
5.1 Major Enhancement: Task-Management
Start of Extract (from Developer Guide)
Task-Management
Tasks are pieces of work to be done or undertaken. Members can create tasks for themselves, and can also be assigned to a task by Exco members.
Current Implementation
The task-management mechanism is facilitated by several command classes in Club Connect, which will be covered in subsequent sub-sections.
Task-management commands require a member to be logged in (and thus by extension, an initial sign-up).
Figure 31 below shows the UML diagram of the Task class.
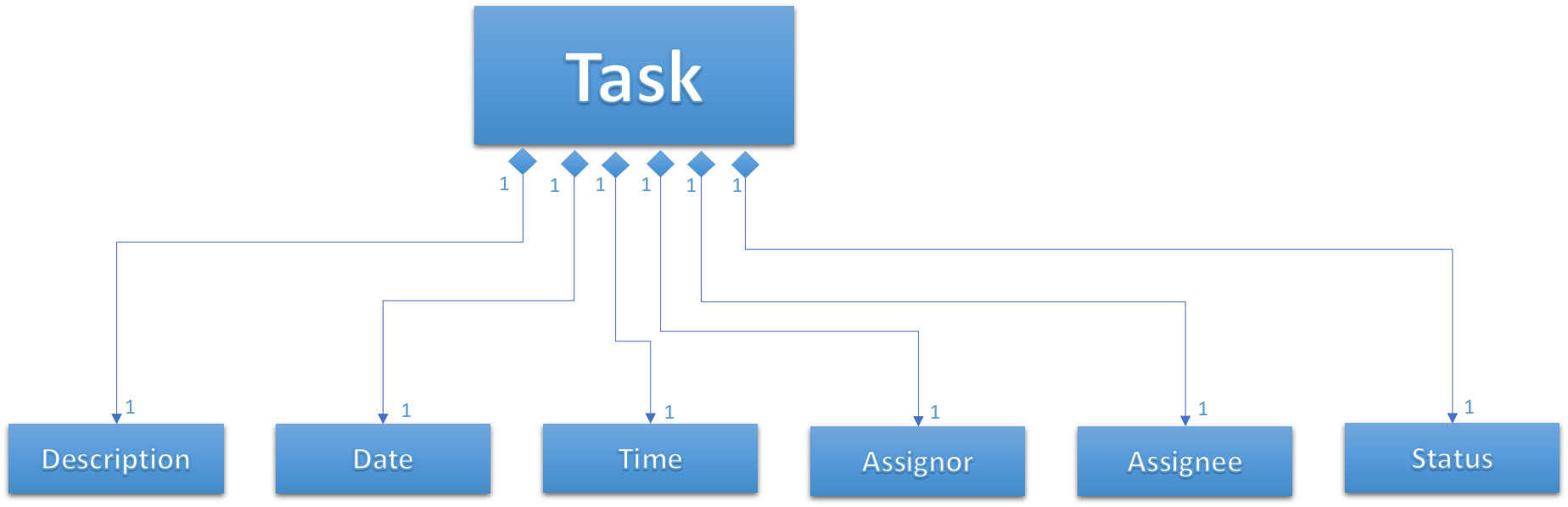
Figure 31. Task UML Diagram
Adding Tasks
Adding Tasks is facilitated by the AddTaskCommand. When this command is invoked, it adds a task with the input Description, Date, and Time. The status of every newly created task is by default set to Yet To Begin. The Assignor and Assignee of the task is set to the Matric Number of the member who is currently logged into Club Connect.
Figure 32 below shows the UML representation of AddTaskCommand.
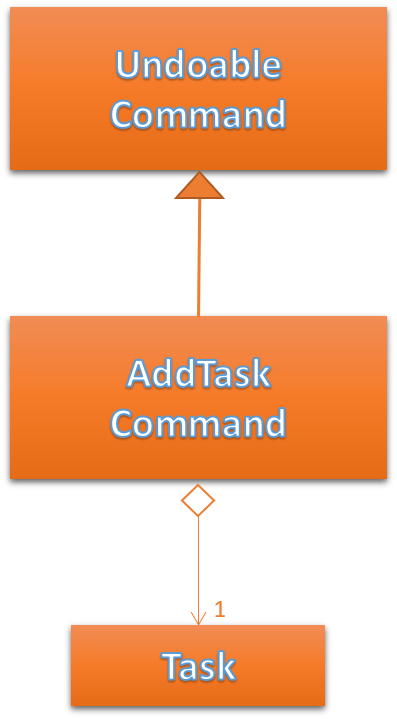
Figure 32. UML diagram of AddTaskCommand.
Figure 33 shows the flow of parsing an AddTaskCommand object:
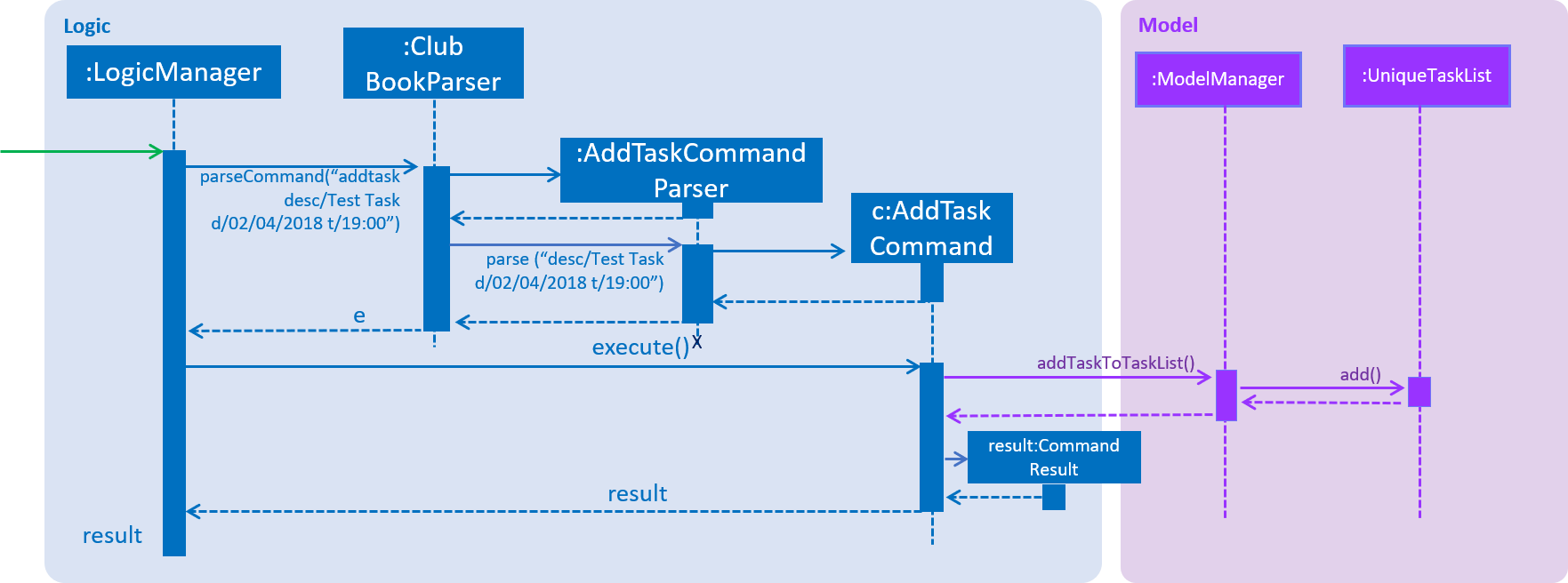
Figure 33. Sequence Diagram for AddTaskCommand parsing.
Figure 34 depicts the high-level sequence of events that take place.
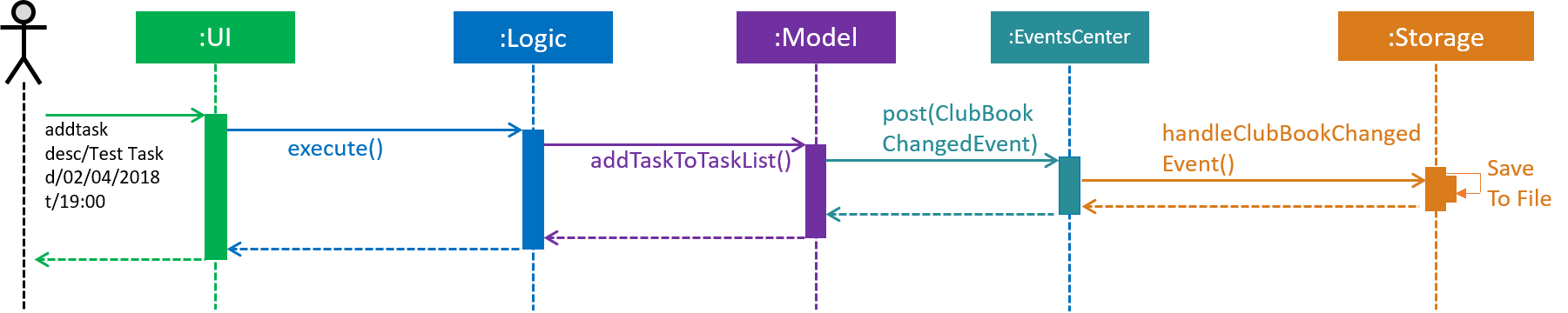
Figure 34. Sequence Diagram for adding a task.
Design Considerations
Aspect: Displaying Assignor and Assignee
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Displays currently logged-in member as Assignor and Assignee.
-
Pros: It is required for
assigntask. -
Cons: Displaying the same matriculation number twice is redundant.
-
-
Alternative 2: Don’t display Assignor and Assignee as it is a personal to-do list.
-
Pros: Takes care of redundancies in Alternative 1 above.
-
Cons: The implementation of
assigntaskbecomes more complex.
-
Changing Task Status
Changing a task’s status is made possible by the ChangeTaskStatusCommand.
Figure 44 below shows the UML representation of ChangeTaskStatusCommand.
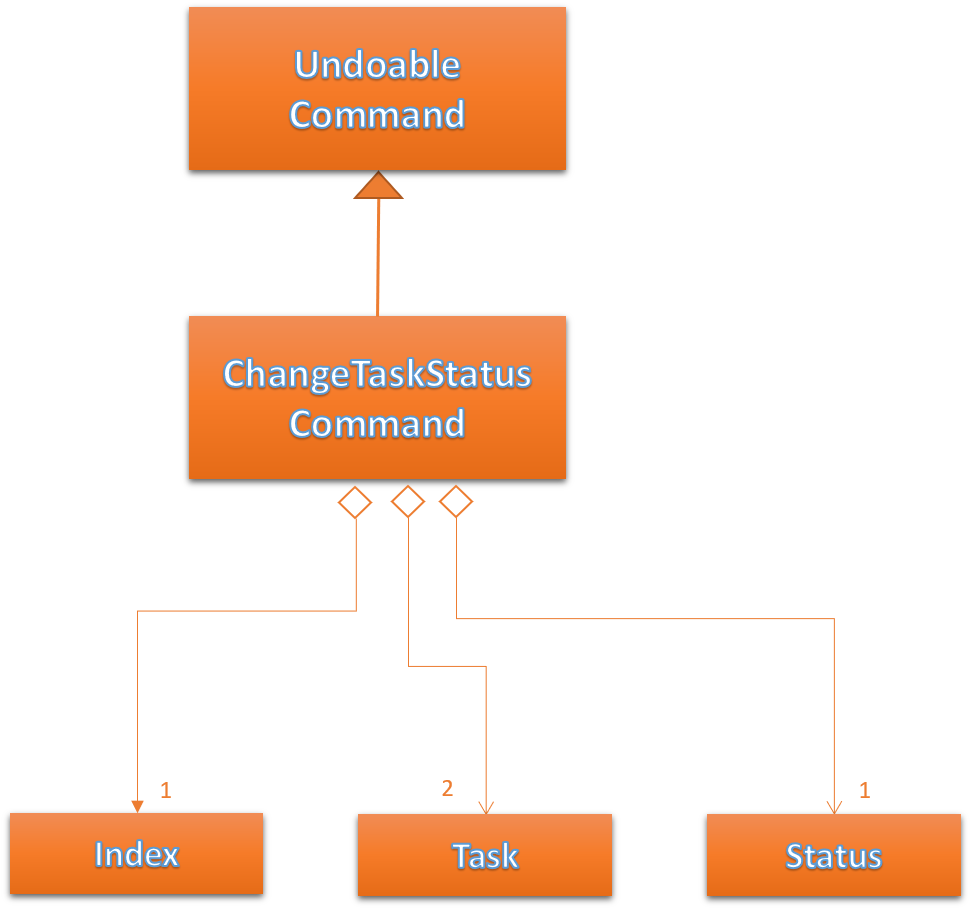
Figure 44. UML Diagram of ChangeTaskStatusCommand.
Parsing of the command is performed by ChangeTaskStatusCommandParser, which returns a ChangeTaskStatusCommand object.
Figure 45 below depicts the parsing of the ChangeTaskStatusObject.
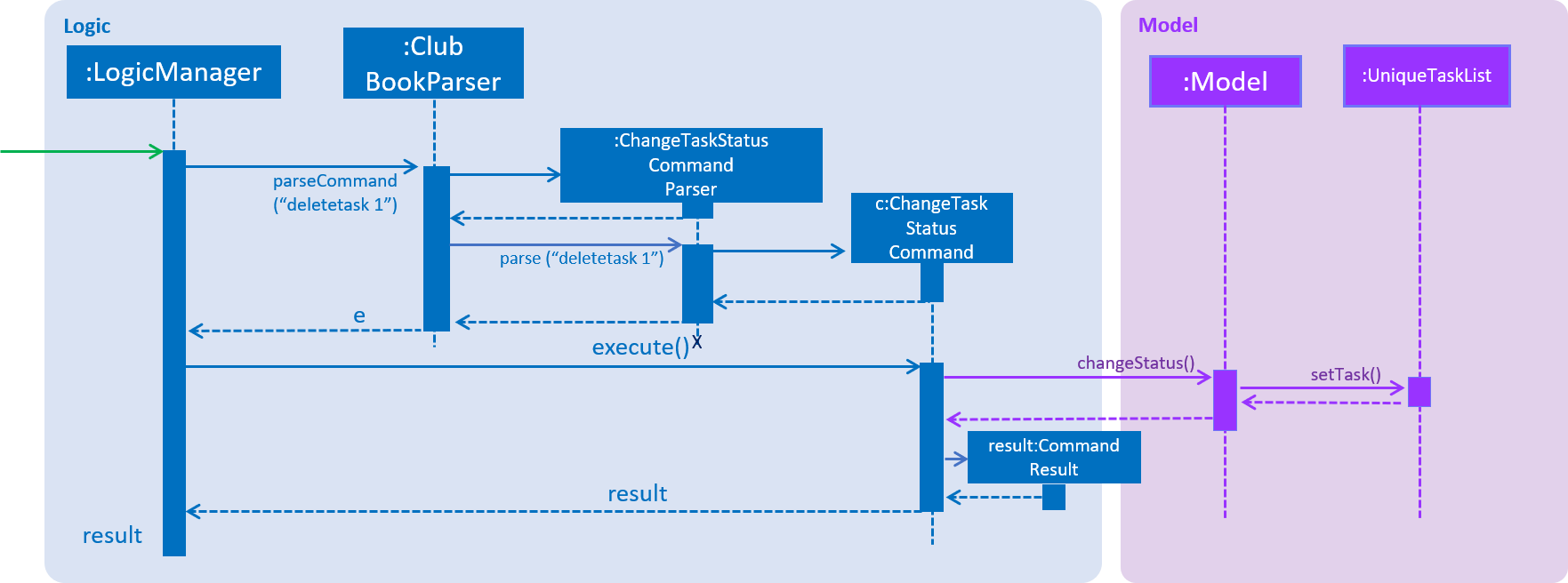
Figure 45. Sequence Diagram for ChangeTaskStatusCommand parsing.
Figure 46 below describes the high-level sequence of events that take place.
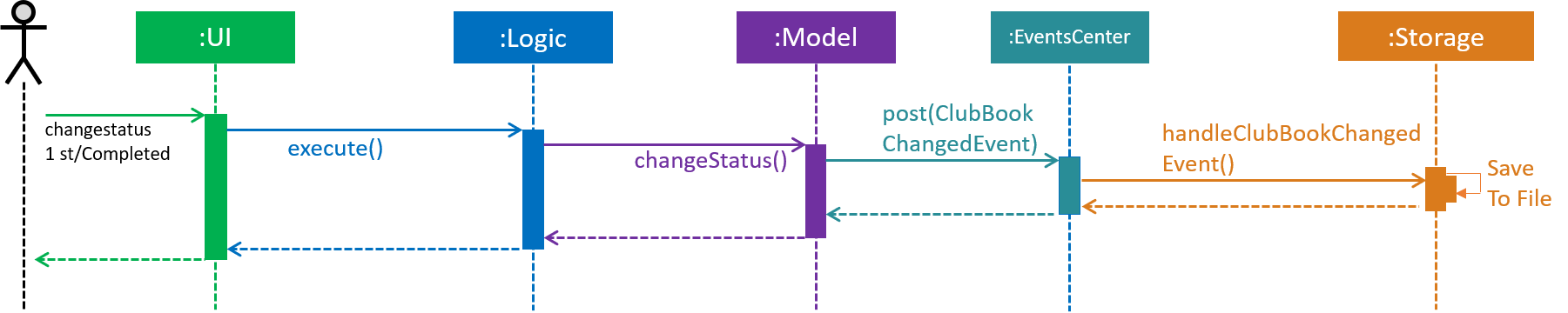
Figure 46. Sequence Diagram for changing the status of a task.
Design Considerations
Aspect: Who can change task status?
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Assignor or Assignee can change the task status.
-
Pros: They are directly associated with the task.
-
Cons: Exco should also have a say.
-
-
Alternative 2: Exco, Assignee or Assignor can change status.
-
Pros: Exco’s powers kept in check.
-
Cons: Exco may misinterpret status of the task.
-
End of Extract (from Developer Guide)
5.2 Minor Enhancement: Delete Group Mechanism
Start of Extract (from Developer Guide)
Delete Group Mechanism
Current Implementation
The deletegroup mechanism is facilitated by the DeleteGroupCommand class. It allows Exco members to delete a group from Club Connect. The group of all members part of the group that is to be deleted will be changed to the default group - member.
The DeleteGroupCommand extends from UndoableCommand as it is an undoable command. Figure 58 below depicts the UML representation of the Command.
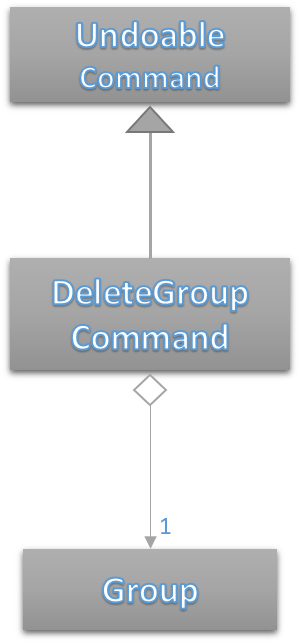
Figure 58. UML Diagram of DeleteGroupCommand.
DeleteGroupCommandParser is responsible for parsing the deletegroup command. It returns a DeleteGroupCommand object after parsing the Group. The parsing of the command is shown below in Figure 59.
The method where the deletion takes place in each member is ClubBook#deleteGroupFromMember.
private void deleteGroupFromMember(Group toRemove, Member member)
throws MemberNotFoundException {
if (!member.getGroup().toString().equalsIgnoreCase(toRemove.toString())) {
return;
}
Group defaultGroup = new Group(Group.DEFAULT_GROUP);
Member newMember = new Member(member.getName(), member.getPhone(), member.getEmail(), member.getMatricNumber(),
defaultGroup, member.getTags());
try {
updateMember(member, newMember);
} catch (DuplicateMatricNumberException dme) {
throw new AssertionError("Deleting a member's group only should not result in a duplicate. "
+ "See member#equals(Object).");
}
}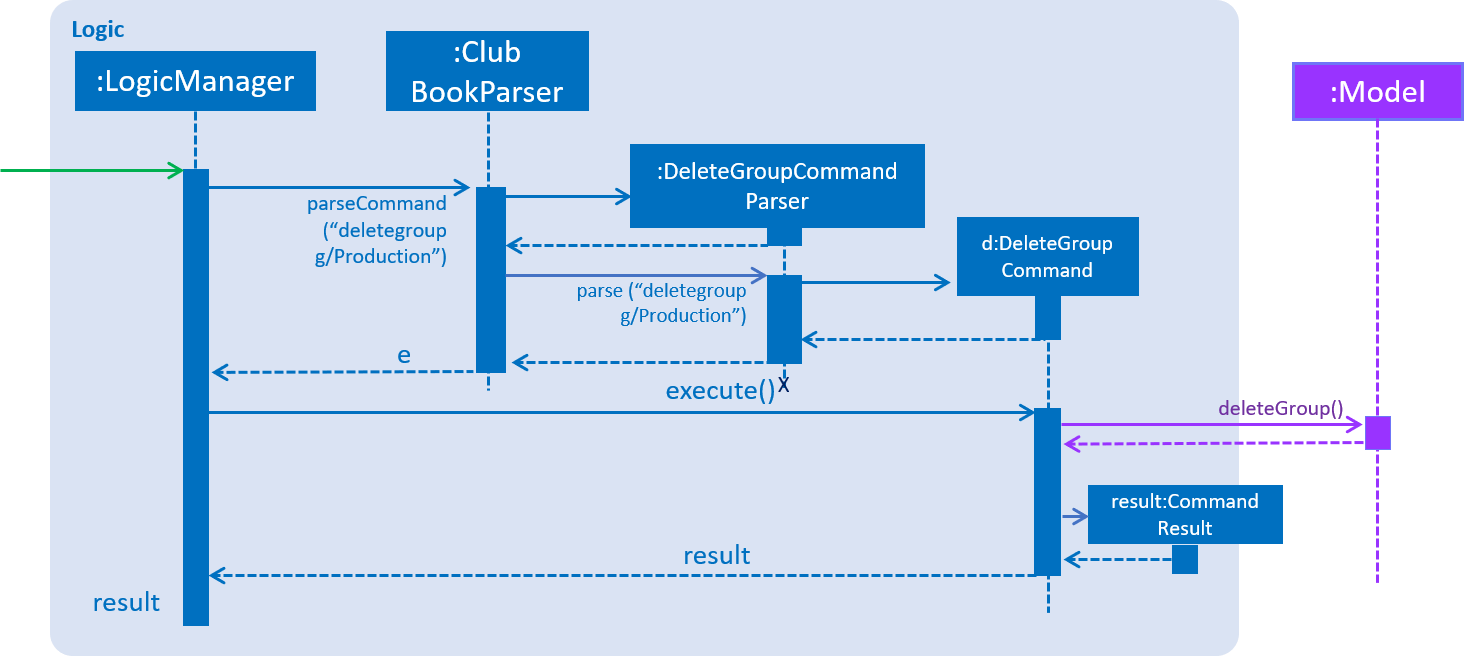
Figure 59. Sequence Diagram for the parsing of DeleteGroupCommand.
The high-level sequence of events is depicted in Figure 60 below.
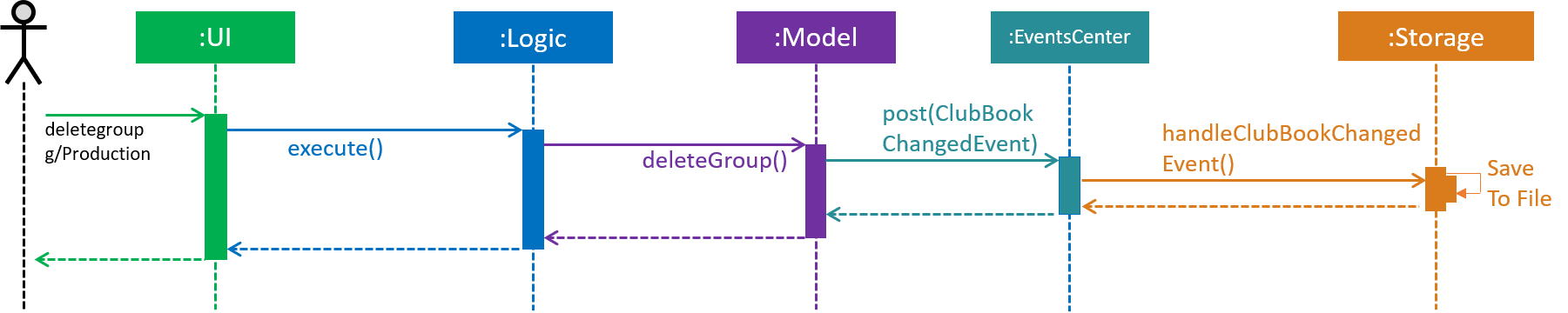
Figure 60. Sequence Diagram for delete a group from Club Connect.
Design Considerations
Aspect: Implementation of DeleteGroupCommand
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Overwrite the relevant
Memberobjects with newMemberobjects.-
Pros: Easy to implement.
-
Cons: Requires looping through all the members in
Club Connect.
-
-
Alternative 2: To maintain a
UniqueGroupList-
Pros: Cleaner implementation.
-
Cons: Relatively difficult to implement.
-
End of Extract (from Developer Guide)
Appendix A : Proposed Enhancement
Data Encryption
External Behaviour
Implementing this feature will have no effect on the functionality that Club Connect provides to its users. The major change that this feature will bring is securing user data. Users can rest assured that none of their data can be leaked to malicious foreign parties.
Justification
Data privacy is a controversial topic in today’s world. When personal data falls into the wrong hands, it can be misused in ways we can’t possibly imagine. Every corporation, organization and service must provide data privacy not only because it’s the law, but also to maintain consumer satisfaction.
Implementation
Start of Extract (from Developer Guide)
[Proposed] Data Encryption
Rationale
Data encryption is key to any App that deals with personal data of individuals.
We plan to use Symmetric Key Encryption to ensure the confidentiality of data.
How Symmetric Key Encryption works
Symmetric key encryption is an encryption philosophy where the two communicating parties share a pre-established secret key k.
It consists of 2 algorithms E (Encrypting or Encoding) and D (Decryption or Decoding) which take in the same key k to perform their respective operations.
The 2 algorithms E and D are efficient algorithms, such that:
-
D(E(k,m)) = m, where 'm' is the message that needs to be kept confidential.
-
For k chosen uniformly at random, E(k,m) gives no additional information about 'm' to an adversary.
Proposed Implementation
We plan to make use of classes that are defined in Javax’s Crypto package.
The classes that would feature in the implementation are:
-
KeyGenerator → constructs a secret (symmetric) key.
-
Cipher → provides the functionality of a cryptographic cipher for encryption and decryption.
The construction of a symmetric key is done by passing the algorithm the encryption will use. The Advanced Encryption Scheme (AES) algorithm is a secure encryption algorithm that has proven been proven secure. A 128-bit AES symmetric key will be used to encrypt all data files.
Once the key is generated, all data will be encrypted with AES. Anyone who wishes to view the decrypted form of the data must possess the secret key.
Figure 74 below describes the encryption procedure used in AES – specifically, the Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) mode.
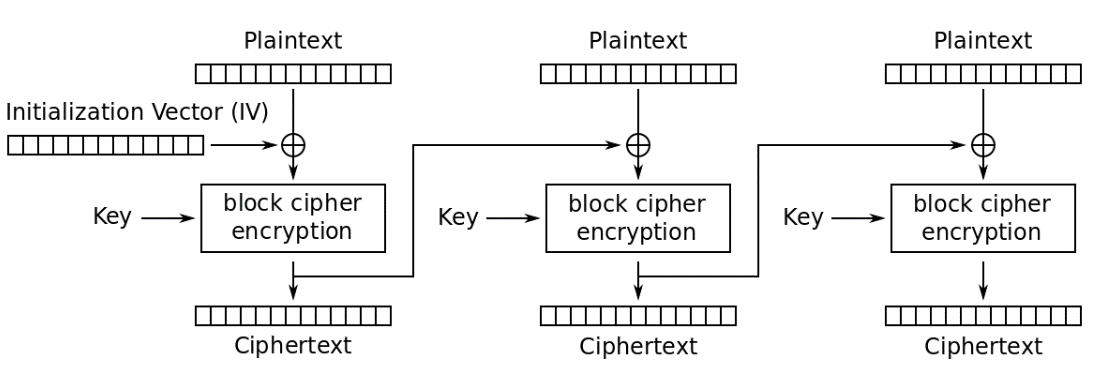
Figure 74. AES – CBC mode encryption.
Figure 75 below shows the decryption process.
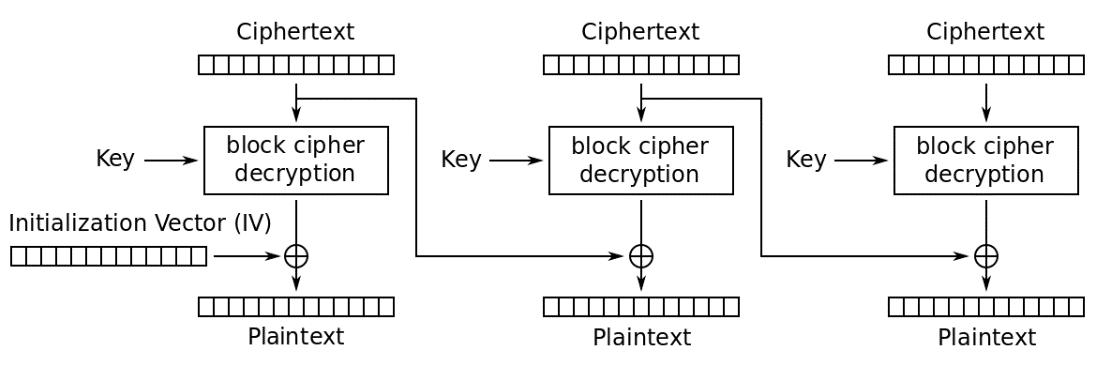
Figure 75. AES – CBC mode decrption.
End of Extract (from Developer Guide)
Appendix B: Other Enhancements and Features
1. Auto-Complete Command Mechanism
Start of Extract (from Developer Guide)
Auto-Complete Command Mechanism
Current Implementation
The auto-complete mechanism is an enhancement added to reduce the frequency pf typos and thus by extension, invalid commands.
It makes use of the key press event KeyEvent. Pressing TAB
The ArrayList<String> commandList in CommandList.java stores all the command formats.
Here is the implementation for handling the key-press event:
private void handleKeyPress(KeyEvent keyEvent) {
switch (keyEvent.getCode()) {
.
.
case TAB:
keyEvent.consume();
completeCommandIndex++;
autoComplete(commandTextField.getText());
break;
.
.
}
}Shown below is the implementation of the autoComplete method.
private void autoComplete(String input) {
if (!input.equals("")) {
if (oldInput == null) {
oldInput = input;
} else if (!input.startsWith(oldInput)) {
oldInput = input;
completeCommandIndex = 0;
}
List<String> completedCommands = LogicManager.COMMAND_LIST.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith(oldInput))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
if (!completedCommands.isEmpty()) {
replaceText(completedCommands.get(completeCommandIndex % completedCommands.size()));
} else {
replaceText("");
}
}
}Design Considerations
Implementation of cycling through commands
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Use string manipulation to store old input and only change it if the new input doesn’t start with the old input.
-
Pros: It’s easy to implement.
-
Cons: It’s not so good in terms of code quality.
-
-
Alternative 2: If there are 'N' commands that start with
XXX, create 'N' strings with each concatenated one after the other in increasing length i.e. XXX1, XXX1XXX2, … ,XXX1XXX2XXX3…XXXN. Keep truncating the commands not needed from the front.-
Pros: Possibly cleaner code.
-
Cons: It’s relatively hard to implement.
-
End of Extract (from Developer Guide)
2. Assign Tasks
2.1 Contribution to User Guide
Start of Extract (from User Guide)
Assigning a task: assigntask (Since v1.4)
Adds a task to Club Connect and assigns it to a member.
Format: assigntask desc/DESCRIPTION d/DUE_DATE ti/TIME m/MATRIC_NUMBER
Alias: assignt
| Duplicate tasks are not allowed. |
This command is for Exco members only.
|
This command assigns the task to the member based on the entered MATRIC_NUMBER.
Examples:
-
assigntask desc/Book PGP Function Room 3 d/02/06/2018 ti/19:00 m/A1234567H
Assigns a task toA1234567Hwith descriptionBook PGP Function Room 3due on02/06/2018at19:00. -
assigntask desc/Buy Food d/03.06.2018 ti/15:00 m/A1122334K
Assigns a task toA1122334Kwith descriptionBuy Fooddue on03/06/2018at15:00.
End of Extract (from User Guide)
2.2 Contribution to Developer Guide
Start of Extract (from User Guide)
Assigning Tasks
Assigning tasks can be accomplished with the AssignTaskCommand. Tasks are assigned to members through the Matric Number attribute.
Figure 35 below shows the UML representation of AssignTaskCommand.
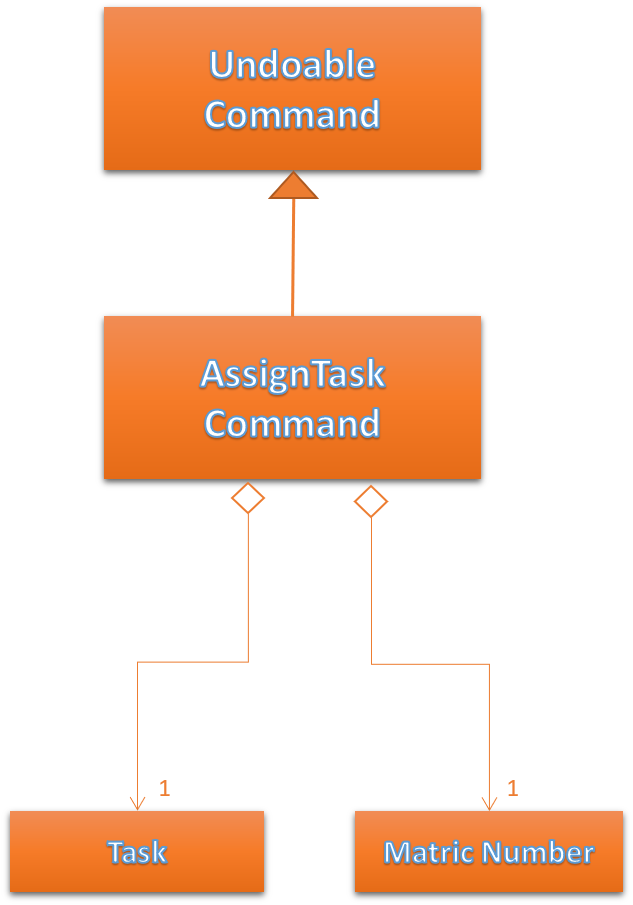
Figure 35. UML diagram of AssignTaskCommand.
The implementation of assigning tasks is similar to that of adding tasks. The only difference is that the Assignor is set to the Matric Number of the member who is currently logged in.
The parsing of an AssignTaskCommand is performed by the AssignTaskCommandParser.
Figure 36 shows the flow of parsing an AssignTaskCommand object:
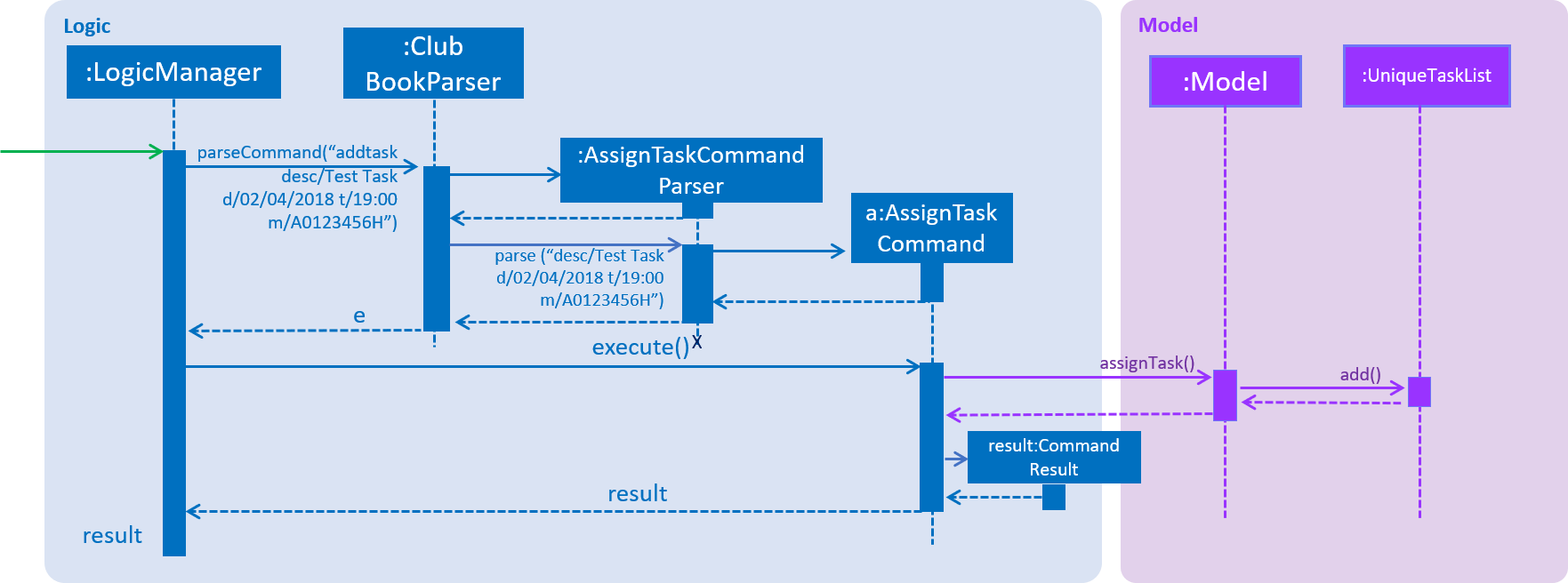
Figure 36. Sequence Diagram for AssignTaskCommand parsing.
Figure 37 depicts the high-level sequence of events that take place.
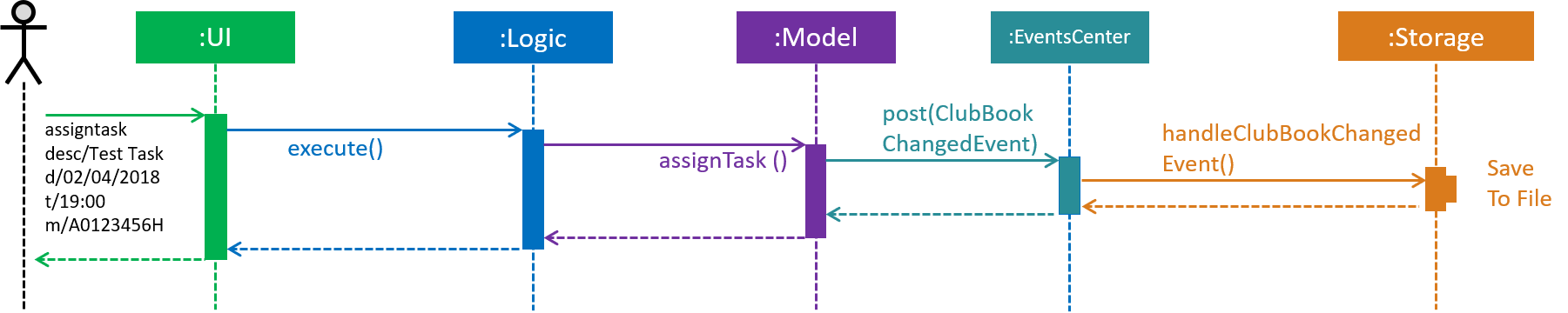
Figure 37. Sequence Diagram for assigning a task.
Design Considerations
Aspect: Displaying similar tasks for different Assignees
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Make a copy of the task for every new
Assigneeif all other parameters are same.-
Pros: Easy to implement
-
Cons: Clutters the
TaskListPanelbecause of redundancies.
-
-
Alternative 2: Maintain a list of
Assignees in a task .-
Pros: Reduces clutter in the
TaskListPaneland is easy on the eye. -
Cons: Relatively difficult to implement.
-
End of Extract (from User Guide)
3. Delete Tasks
3.1 Contribution to User Guide
Start of Extract (from User Guide)
Deleting a task : deletetask (Since v1.3)
Deletes the specified task from the club book.
Format: deletetask INDEX
Aliases: deltask, rmtask
Only Members who are the Assignor can delete their respective tasks.
|
Examples:
-
viewmytasks
deletetask 2
Deletes the 2nd task in the results of theviewmytaskscommand. -
viewalltasks
deletetask 1
Deletes the 1st task in the results of theviewalltaskscommand.
End of Extract (from User Guide)
3.2 Contribution to Developer Guide
Start of Extract (from Developer Guide)
Deleting Tasks
The 'DeleteTaskCommand` is used to delete a task. A task can only be deleted if the member who is currently logged in is either the Assignor or the Assignee.
The command object takes in the INDEX of the task to be deleted.
Figure 38 below shows the UML representation of DeleteTaskCommand.
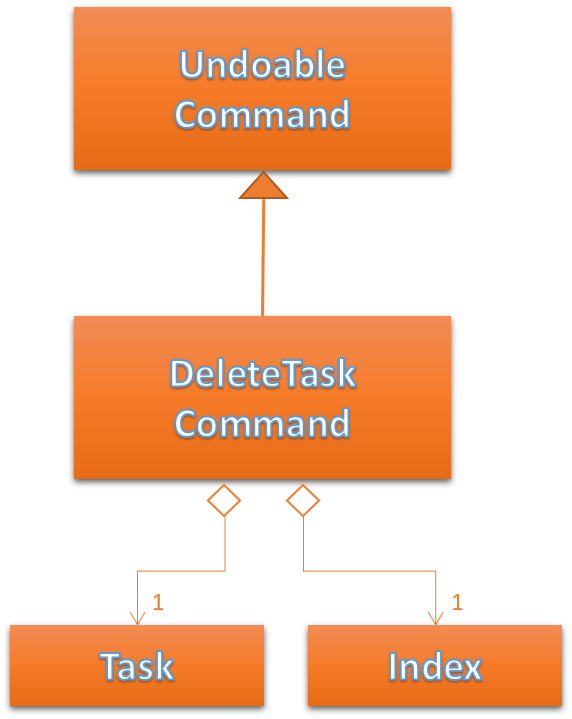
Figure 38. UML diagram of DeleteTaskCommand.
DeleteTaskCommandParser is responsible for parsing the user input into a DeleteTaskCommand object.
Figure 39 illustrates the sequence in which the parsing is done.
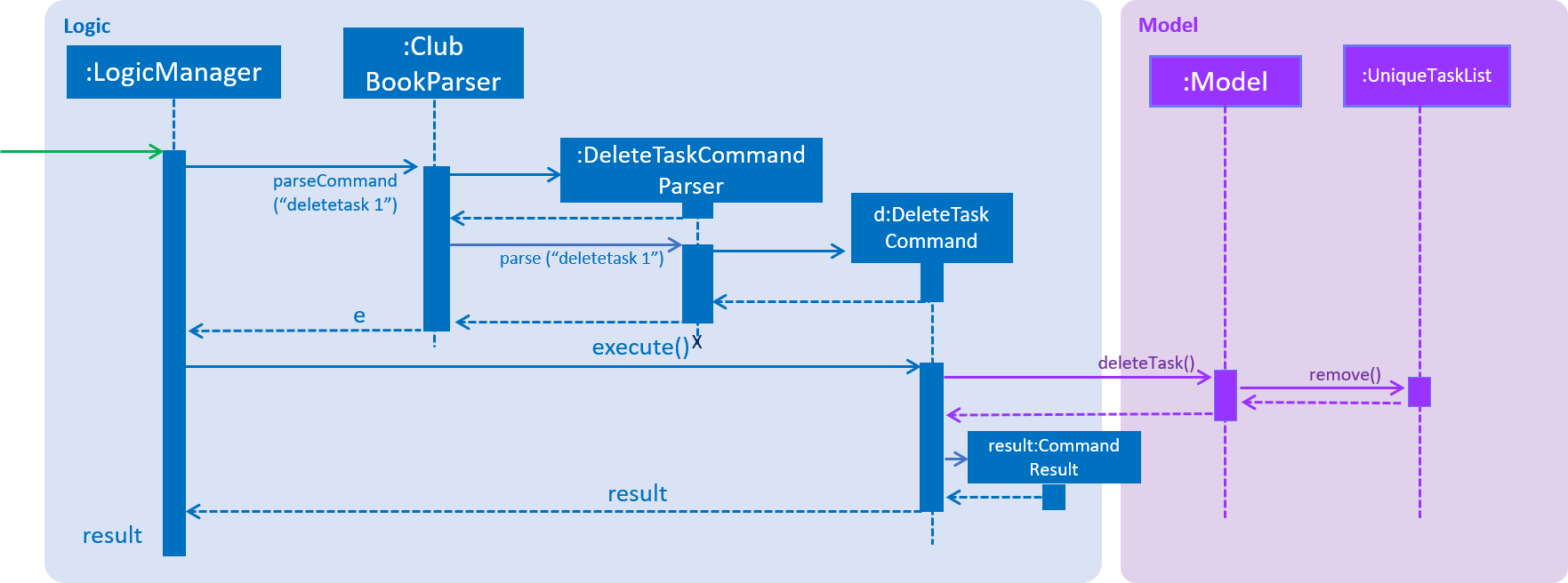
Figure 39. Sequence Diagram for DeleteTaskCommand parsing.
The high-level sequence of events is shown below in Figure 40.
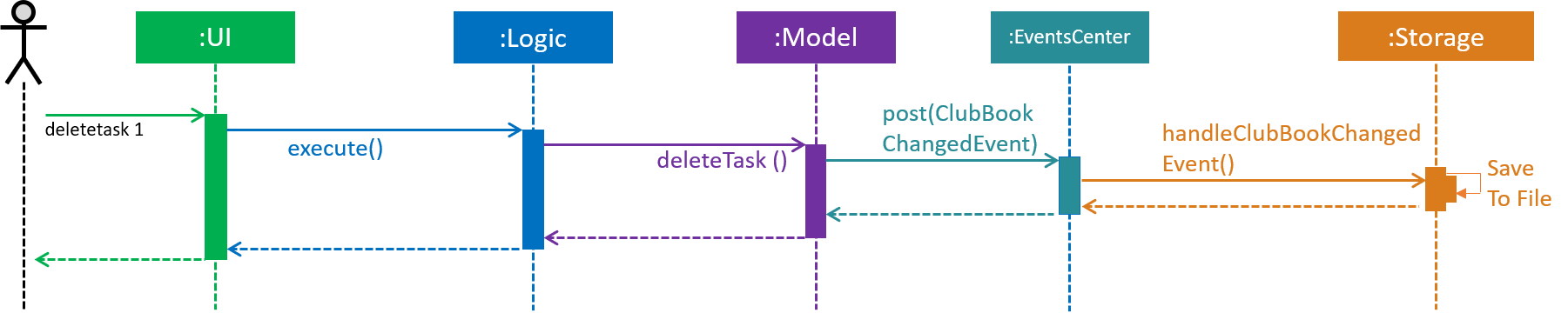
Figure 40. Sequence Diagram for deleting a task.
Design Considerations
Aspect: Who can delete tasks?
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Only Assignors can delete tasks.
-
Pros: It improves accountability of the club.
-
Cons: All the workload falls on the Assignor.
-
-
Alternative 2: Assignor or Assignee can delete task.
-
Pros: The workload is evenly distributed.
-
Cons: Reduces transparency of club and accountability of club members.
-
End of Extract (from Developer Guide)
4. Changing task assignee
4.1 Contribution to User Guide
Start of Extract (from User Guide)
Changing the assignee of a task : changeassignee (Since v1.5rc)
Changes the assignee of a task in Club Connect.
Format: changeassignee INDEX m/MATRIC_NUMBER
Alias: assignee
This command is only for Exco members.
|
Examples:
-
changeassignee 1 m/A0123456H
Changes the assignee of the 1st task toA0123456Hin the task listing. -
assignee 3 m/A6656789H
Changes the assignee of the 3rd task toA6656789Hin the task listing.
End of Extract (from User Guide)
4.2 Contribution to Develop Guide
Start of Extract (from User Guide)
Assigning Tasks
Assigning tasks can be accomplished with the AssignTaskCommand. Tasks are assigned to members through the Matric Number attribute.
Figure 35 below shows the UML representation of AssignTaskCommand.

Figure 35. UML diagram of AssignTaskCommand.
The implementation of assigning tasks is similar to that of adding tasks. The only difference is that the Assignor is set to the Matric Number of the member who is currently logged in.
The parsing of an AssignTaskCommand is performed by the AssignTaskCommandParser.
Figure 36 shows the flow of parsing an AssignTaskCommand object:

Figure 36. Sequence Diagram for AssignTaskCommand parsing.
Figure 37 depicts the high-level sequence of events that take place.

Figure 37. Sequence Diagram for assigning a task.
Design Considerations
Aspect: Displaying similar tasks for different Assignees
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Make a copy of the task for every new
Assigneeif all other parameters are same.-
Pros: Easy to implement
-
Cons: Clutters the
TaskListPanelbecause of redundancies.
-
-
Alternative 2: Maintain a list of
Assignees in a task .-
Pros: Reduces clutter in the
TaskListPaneland is easy on the eye. -
Cons: Relatively difficult to implement.
-
End of Extract (from User Guide)
5. Viewing Tasks
5.1 Contribution to User Guide
Start of Extract (from User Guide)
Viewing all tasks in Club Connect : viewalltasks (Since v1.4)
Displays all the tasks created/assigned in Club Connect. This is a command that can be used by Exco members to monitor all the tasks in the club.
Format: viewalltasks
Alias: alltasks
This command is for Exco members only.
|
Viewing tasks assigned to or assigned by you : viewmytasks (Since v1.4)
Display all tasks created/assigned by the currently logged-in member in Club Connect.
The main purpose of this command is to enable Exco members to toggle between all tasks and those related to them. |
Format: viewmytasks
Alias: mytasks
End of Extract (from User Guide)
5.2 Contribution to Developer Guide
Start of Extract (from Developer Guide)
Viewing All Tasks
Exco members can view all the tasks in Club Connect using the ViewAllTasksCommand.
The high-level sequence of events on executing the ViewAllTasksCommand is described below in Figure 47.
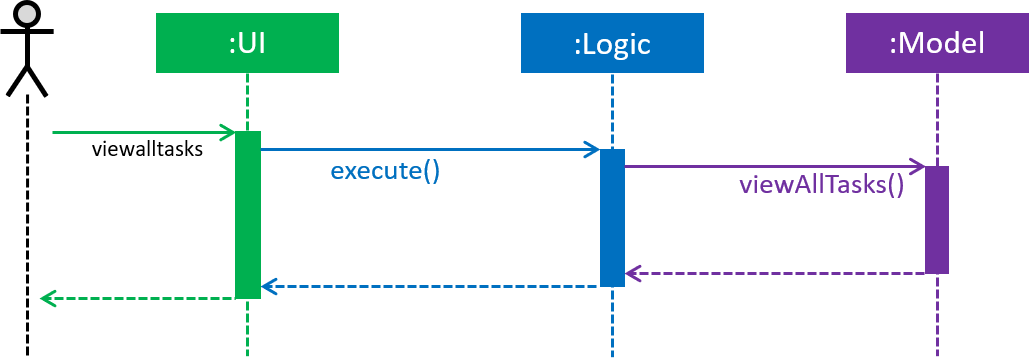
Figure 47. Sequence Diagram for viewing all tasks.
Viewing My Tasks
Exco members need a way to toggle between all tasks in Club Connect and the tasks that are related to them (i.e. tasks that they have assigned or been assigned to). This is achieved by the ViewMyTasksCommand.
The Predicate used is TaskIsRelatedToMemberPredicate. Here is the overridden TaskIsRelatedToMemberPredicate#test method.
@Override
public boolean test(Task task) {
return member.getMatricNumber().toString().equalsIgnoreCase(task.getAssignor().getValue())
|| member.getMatricNumber().toString().equalsIgnoreCase(task.getAssignee().getValue());
}The sequence diagram of the viewmytasks command is shown below in Figure 48.
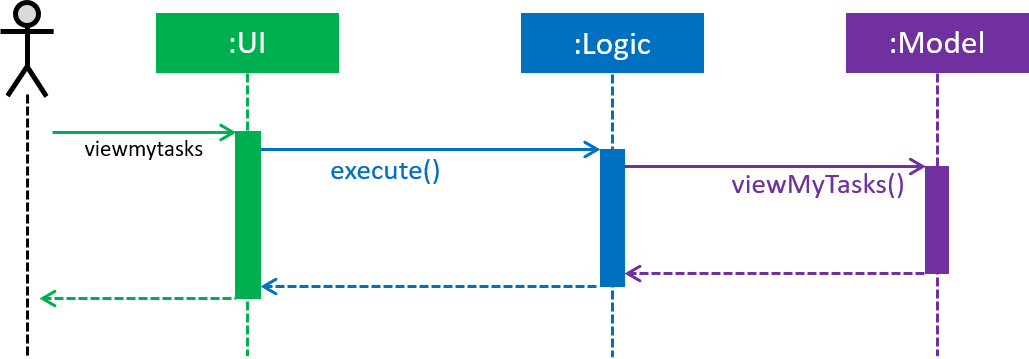
Figure 48. Sequence Diagram for viewing tasks of the currently logged-in member.
End of Extract (from Developer Guide)